The Porter’s value chain model was developed by Michael Porter in 1985 to depict how customer value accumulates along a chain of activities that lead to an end product or service.
- The value chain model serves as a basic tool for diagnosing competitive advantage and finding ways to enhance. It identifies technologically and economically distinct activities called value activities that an organization performs in the course of doing business.
- The model is used to know, how optimally the organization’s resources are used.
- The model highlights specific activities in the business through which organizations can create value and get a competitive advantage by applying competitive strategies.
- The model helps to analyze where information systems are most likely to have a strategic impact.
- The model views an organization as a chain or network of basic activities and each activity and each activity in the chain adds value to the final product\service.
Porter’s Value Chain Model
Through this model, the idea to consider the processes as complete entities and not as something that occurs within the respective departments of an organization was brought forward by a porter.
The model of the value chain can be expressed as:
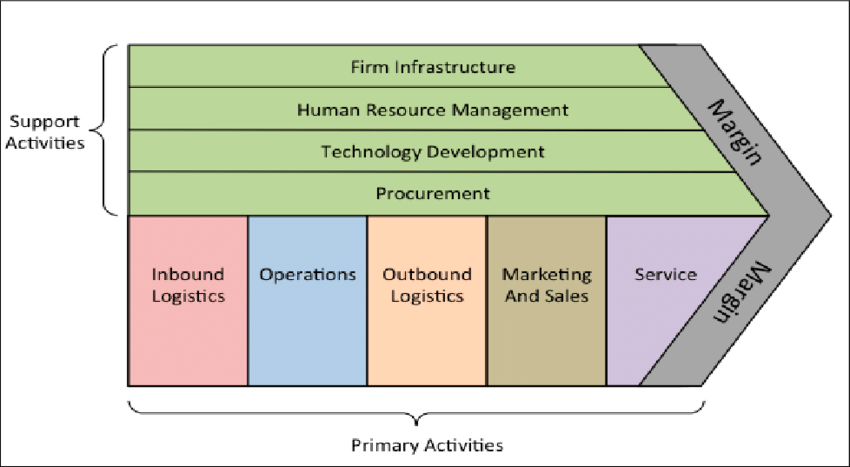
This model can be used to do company analysis in which, one can systematically evaluate a company’s key processes and core competencies. In this analysis, one can first determine the strengths and weakness of performing the activities and the value added by each activity.
Some of the activities may add more value and might provide a strategic advantage. This will help an organization to critically examine the value-added activities at each stage and thus suggests whether to improve the business processes or drop the business processes.
According to Porter’s value chain model, the activities conducted in any organization can be divided into two categories: Primary activities and support activities. These value activities form a bridge between competitive strategy formulation and implementation.
Primary Activities:-
The primary activities are those business activities that relate to the production and distribution of the firm’s products and services, thus creating value for which customers are willing to pay. Primary activities involve purchasing materials, into products and delivering products to customers.
The five primary activities are:
-
Inbound logistics(inputs)
-
Operations (manufacturing and testing)
-
Outbound logistics (storage and distribution)
-
Sale and Marketing
-
Customer services (after-sales services)
The primary activities usually take place in a sequence from 1 to 5. As work progresses according to the sequence, a value is added to the product or service in each activity. To be more specific, the incoming materials are processed (in receiving, storage etc.) and in this process, a value is added to them in activities called inbound logistics.
Next, the material is used in operations, where significant value is added by the process of turning raw material into products. The products need to be prepared for delivery (packing, storing and shipping) in the outbound logistics activities and so more value is added in the activities.
The sale and marketing attempt to sell the products to customers, increasing product value by creating demand for the company’s products. Finally, customer services, such as warranty service or upgrade notification, is performed the customer, further adding value. All of these value adding, primary activities result in profit.
Support Activities:-
The primary activities are supported by support activities. Unlike primary activities, support activities do not add value directly to the firm’s products or services. Rather, supporting the primary activities.
Support activities consist of:
-
Corporate infrastructure
-
Human resources
-
Technology development
-
Procurement
Each support activity can support any or all of the primary activities and the support activities may also support each other. These activities are described below:
-
Corporate infrastructure:-
This activity is the backbone of the business unit. It includes general management, accounting, finance, planning, legal services, and quality management.
-
Human resources:-
Human resource management is concerned with recruiting, training and advancing the careers of people who work for the firm. The output of this activity affects virtually every other activity in the company.
-
Technology development:-
Technology also applies to the support of the value chain through all of its steps. This activity adds value in the way it improves the product and the business processes in the primary activities.
-
Procurement:-
Procurement deals with obtaining the raw materials needed to produce a product or service. Thus this activity focuses on the purchasing function and ensures the availability of quality raw material for production.
Also Read:-
What do you mean by e-commerce?